Texas Holdem Hands Chart
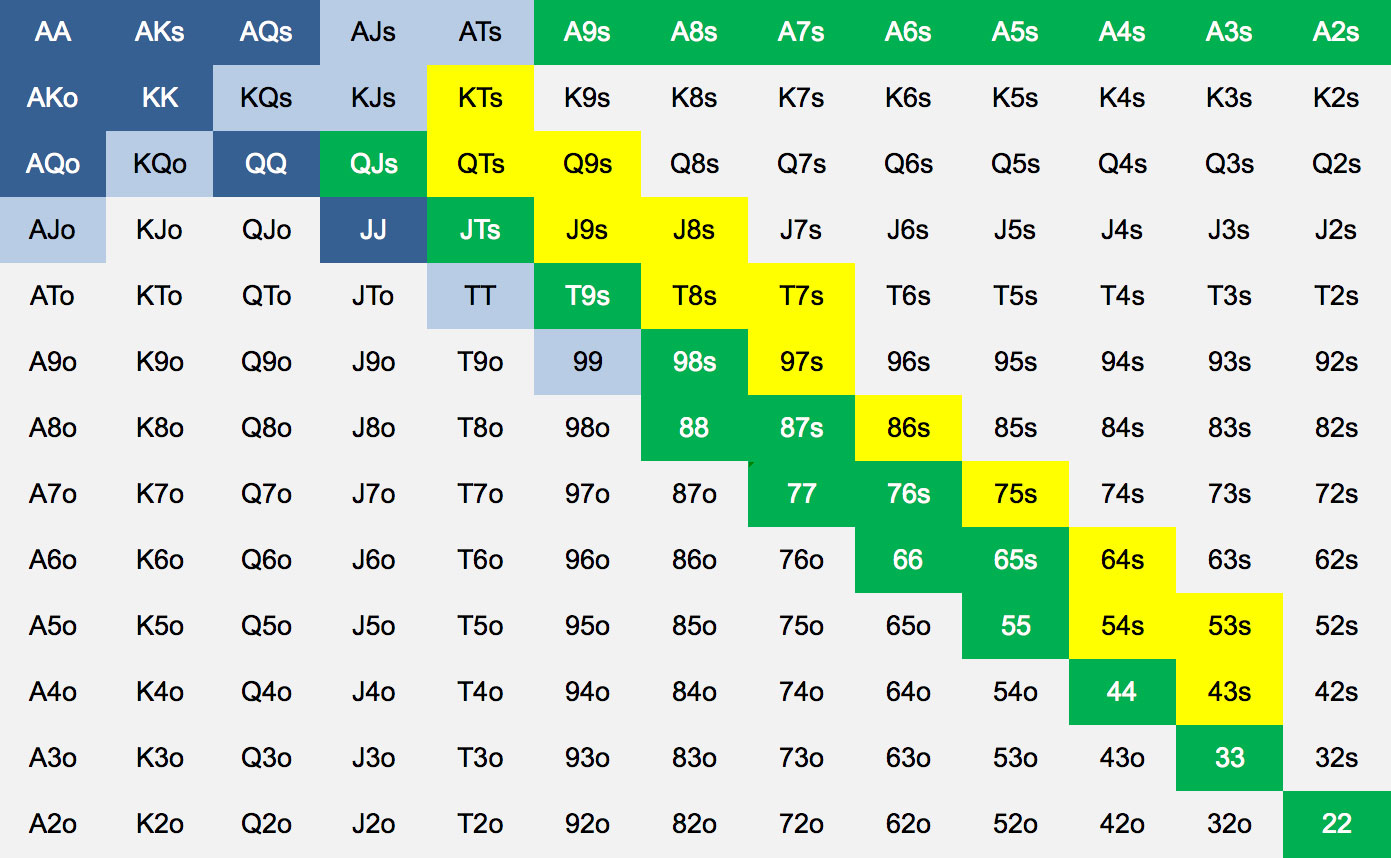
Print out this free poker hand rankings chart – and always know the best winning poker hands. Poker hands are ranked in order from best to worst. Royal Flush An ace high straight flush. Straight Flush Five consecutive cards in the same suit. Four of a Kind Four cards of the same rank.
For a certain segment of new hold’em players, starting hand charts can be fascinating. Even those with many years of experience who have little need to consult such charts still find them interesting as debate-starters.
In hold’em there are 169 different combinations of hands you can be dealt. For those of us who enjoy working with numbers or creating lists with which to organize our lives, there’s something appealing about the idea of ranking all of those hands from 1 to 169, even if we know such a list probably might have only limited value when it comes to actual game play.
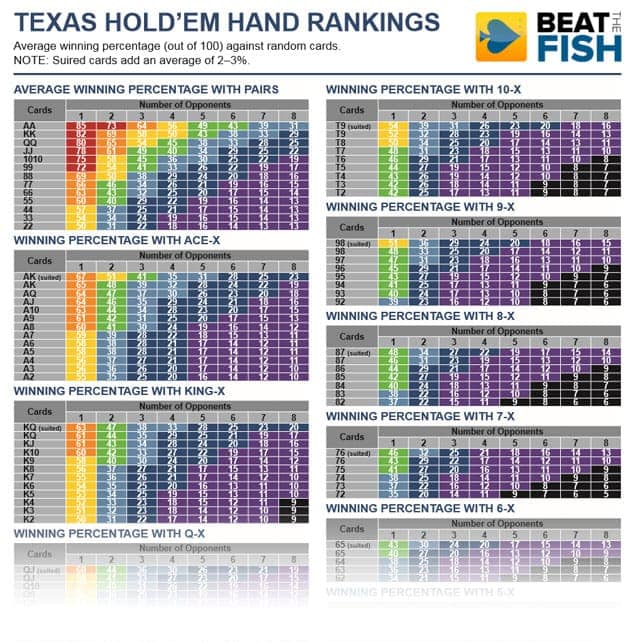
- Poker Hand Rankings & Charts: Evaluate Your Poker Cards. Before you take us up on our free poker money offer on your way to becoming a World Series of Poker champion, you must first master the basics. The most important in the game is to understand the poker hand strength and rankings.
- Also ensure that you have checked Texas Holdem No Limit Starting Hands Chart the terms and conditions of a given bonus well in advance. Provided you meet a casino’s requirements regarding a particular bonus, you could benefit from extra casino cash, free spins as well as an opportunity to win even bigger prizes.
In truth, there are actually a lot more possible combinations of hole cards in hold’em — 1,326 of them, in fact. But that total also considers suits as distinct, when in fact before the community cards come the suits are all essentially of equal value.
That is to say, is of the same value as when playing preflop, while and are also of equivalent value. So, too, are the different combinations producing the same pocket pairs all equal before the flop in terms of their relative worth. While there are six different ways to get pocket aces — , , , , , — you're equally happy no matter what suits the cards are.
So we get rid of all of those redundant hands and say that in Texas hold'em there are 169 “non-equivalent” starting hands, breaking them down as follows:
- 13 pocket pairs
- 78 non-paired suited hands (e.g., with two cards of the same suit like or )
- 78 non-paired unsuited hands (e.g., with two cards of different suits like or )
Notice now the non-paired combinations of hole cards neatly divide into equal groups, both of which are six times as large (78) as the smaller group of pocket pairs (13). The total of 169 combinations represents a square, too — 13 x 13 — another curious symmetry when it comes to hold'em hands.
Still, that’s a lot of starting hand combinations — too many for most of us humans to keep in our heads — which is one reason hand ranking charts are appealing and even can be useful, since they help players think about certain two-card combos as “strong” or “average” or “weak” as possible starters.
Setting aside the idea of actually ranking the 169 hands from best to worst, we might think for a moment about other ways of categorizing starting hands in hold’em, using that initial breakdown of hands into pocket pairs, non-paired suited hands, and non-paired unsuited hand as a first step toward coming up with further, smaller groups that are easier to remember.

The 13 pocket pairs we might group as big or “premium” (, , and ), medium ( through ), and small ( through ).
Meanwhile, we might divide each of the other groups into “connectors,” “one-gappers,” and “two-gappers” (and so on), further thinking of them also as “big,” “medium,” and “small” while also keeping separate suited and non-suited combinations.
These categories of non-paired hands are created by thinking about straight-making possibilities (affected by connectedness) and flush-making possibilties (affected by suitedness). There are more ways to make straights with “connectors” — that is, two cards of consecutive rank like — than with two-gappers, three-gappers, and so on. So, too, do you have a better chance of making a flush with suited hole cards than with non-suited hole cards.
Another possible group to create would include “ace hands” — i.e., non-paired hands containing one ace — that can be thought of as “big aces” (e.g., , ), “medium aces” ( down to ), and “small aces” ( to ). Or “king hands,” too. We like keeping these groups in mind, as hands with big cards like an ace or king can connect with flops to make big pairs.
In any case, you can see how these criteria for making categories can help when it comes to building those starting hand charts. And in fact most of those charts feature a similar ordering of hands, with...
- the premium pocket pairs and the big aces (suited and non-suited) up at the top;
- medium and small pocket pairs and big-to-medium suited connectors and one-gappers in the middle;
- and non-paired hands with less potential to make big pairs, straights, or flushes toward the bottom.
Would you like to get your hands on a free $10k entry to the WSOP Main Event?
Click on the link below and enter your email to participate to the free giveaway and take a shot at this massive opportunity!
Play NowHowever, there are problems with relying so heavily on starting hand charts that you don’t take into account factors that can make a given hand gain or lose value. Such as the flop. Or the turn. Or the river. Or other factors — including how your opponents are playing their hands — that can quickly affect the value of your starting hands.
After all, as anyone who’s played even a few hands of hold’em well knows, even if is the highest-ranking starting hand and a non-suited ranks as 169th, a couple of deuces among the community cards is all it takes to make the best hand worst and the worst hand best.
Learning the relative value of starting hands is definitely an important first step when it comes to getting started in hold’em. Other aspects of game play such as the importance of position, knowing when and how much to bet or raise, and thinking about opponents’ holdings and playing styles as hands proceed are good to learn, too, and help show how a great starting hand might not be so great five community cards later.
Poker is not blackjack, a game in which similar hand-ranking guides are sometimes used to inform players’ decisions about how to play. In poker you want to be wary about becoming too reliant on those pretty starting hand charts. They can be great for indicating which hands might be worth playing (and which should be thrown away), but troublesome if allowed to outweigh all of the other important factors that arise as a hand plays out.
That said, starting hand charts can be useful, especially for those new to hold’em. They also can be a big help when picking up other games, too, like pot-limit Omaha or the various stud games, if only to get an early idea what hands tend to play better than others.
But for many such charts ultimately are only themselves a way to get started, before the experience of playing helps players more instinctively recognize both hand groupings and how hands tend to compare in terms of profitability.
Get all the latest PokerNews updates on your social media outlets. Follow us on Twitter and find us on both Facebook and Google+!
Tags
no-limit hold’emcash game strategytournament strategybeginner strategystarting hand selectionstarting hand chartsmath
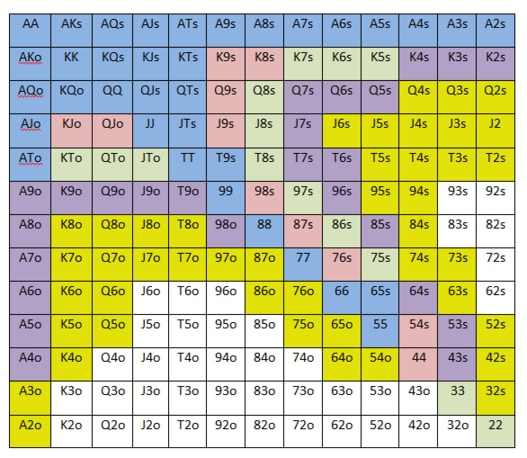
NL Hold’em Starting Hand Charts
One aspect of the game of No-Limit Hold’em that causes beginning players much grief is deciding which hands to play and which hands to dump. NL Hold’em is much more difficult than Limit Hold’em because the value of a hand depends on so many factors other than just the cards in your hand. Despite this difficulty, our coaches believe that following some general guidelines and adjusting from these is a better solution than having no guidelines at all. Given that well over half of your profitability in NL Hold’em is based on hand selection alone, we have developed these charts to help you better determine whether to play or fold.
There are no perfect No-Limit starting hand charts. That is because there are many factors that affect your decision, and charts cannot account for all of them. Some of these include:
- The size of your opponent's stacks.
- How loose or tight, passive or aggressive, your opponents are.
- Where these opponents are located at the table – for example, does an aggressive player still have to act after you?
- Your image at the table – for example, how tight or tricky you are perceived.
That being said, these charts will serve you well in most typical low-stakes No-Limit cash games, such as games with blinds of $1/$2, and home games. These games typically have several loose players at the table, and good opportunities for winning big pots with suited connectors and pocket pairs. With practice, you will be able to be a consistently winning player with these charts as a starting point. As you improve, you'll find yourself making adjustments to these charts based on the factors listed above, and more.
AGAIN: These charts are a good starting point for beginners. Specifically, Chart #1 recommends a significant amount of limping. This is great in loose, passive games but less often seen in tougher games. You’ll find other training material on Advanced Poker Training that may recommend a more aggressive approach for more experienced players.
Note: It would be a serious mistake to apply these hand charts before reading the Frequent Asked Questions first.
CHART #1 ‐ LOOSE, PASSIVE GAME (OFTEN 4-5 LIMPERS PER HAND)
NO ONE HAS RAISED YET
- Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise raise
- Call always
- Call from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
CHART #2 ‐ TIGHTER GAME (FEWER LIMPERS) OR MORE AGGRESSIVE GAME
NO ONE HAS RAISED YET
- Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise raise
- Call (or Raise) from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
CHART #3 ‐ THERE HAS BEEN A SINGLE RAISE
(3‐5 TIMES THE BIG BLIND) BEFORE YOU
- Re‐Raise Always
- Call from Early Position, otherwise re‐raise
- Call always
- Call from Middle or Late Position if the conditions are right (see Frequently Asked Questions)
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
For the hands in yellow, what do you mean when you say to play these hands if the conditions are right? The hands in yellow are speculative hands. They should always be folded from Early Position. From other positions, they can be profitable given the right conditions. Some of the questions to ask yourself:
- Are there other players who have called so far (the more, the better)?
- Are the players who have called playing poorly after the flop? Will they pay me off if I hit something?
- Is there an aggressive player still to act behind me (you might get raised and have to fold)?
- If there has been a raise and no other callers, what chance do I have of using my position after the flop to win the hand even if I don't improve (Chart #3 only)?
Why does Chart #2 say to sometimes raise with the hands in yellow, but Chart #1 does not? We have different goals in mind. Using Chart #1, we want to call to encourage additional players to enter the pot. These hands will be immensely profitable when our loose, passive opponents enter the hand, and get trapped when we flop a set, or make a well-disguised straight. When using Chart #2, however, we want to size up the opponents still to act. If they are tight, we can raise. Sometimes, we'll pick up the blinds. Other times, our pre-flop aggression will allow us to take down the pot on the flop.
What's the difference between AKs and AKo? AKs means an Ace and King of the same suit. AKo means an Ace and King of different suits.
What are early, middle, and late position? Early Position is generally the first 2 (in a nine player game) or 3 (in a ten player game) positions after the blinds. Late Position is the “cutoff” position (to the right of the dealer), and dealer button positions. Middle Position is everything in between.
How much should I raise? As a general rule, raise 3 to 4 times the big blind, plus 1 extra big blind for every player who has called before you. So if there are 2 callers already, raise between 5 and 6 times the big blind.
What if someone raises after I call? Whether you call the raise depends on how much money the raiser has for you to win, how many other players are involved, and what type of hand you have. As a general rule, if you have a pocket pair, lean towards calling. If there are a lot of other players (and therefore a big pot), lean towards calling. In general, fold suited connectors from early position. Fold hands like KQ that don't play well against a raiser.
Texas Holdem Playable Hands Chart
How do I play from the blinds? From the small blind, play the same hands you would play from late position, plus a few more. But don't call with junk hands like T5o, just because it is “cheap”. From the big blind, if there is a raise to you, play like you would if you had already called from early position.
The chart says to fold KQo to a raise. Really? Yes, this hand performs very poorly against typical raising hands. Against AK, AQ, AA, KK, QQ, you are a big underdog. Other typical raising hands like JJ, TT, 99, AJs, are slightly ahead of you as well. The only time you might call or re-raise is from late position, if the opener was in middle or late position, indicating they might have a wider range of hands.
I was told to fold AJo from Early Position, why do you say to call with it? Folding AJo is not a bad idea in many games. We included it because, at low stakes tables (even tight or aggressive ones), the players are often playing badly enough after the flop that it can be profitable. We used data from millions of hands of low-limit poker to analyze this. The same could be said for KQo, ATs, and KJs – you can make a small profit in the long run at most low-stakes games, but folding would be perfectly acceptable from early position.
Can I use these charts in a NL Hold'em tournament? The charts would be best applicable to the early stages of a NL tournament, when everyone has a deep stack. In the middle and later stages, they should not be used.